10 System Design Patterns That Actually Matters (Inspired by ByteByteGo)
10 System Design Patterns Every Software Engineer Should Know
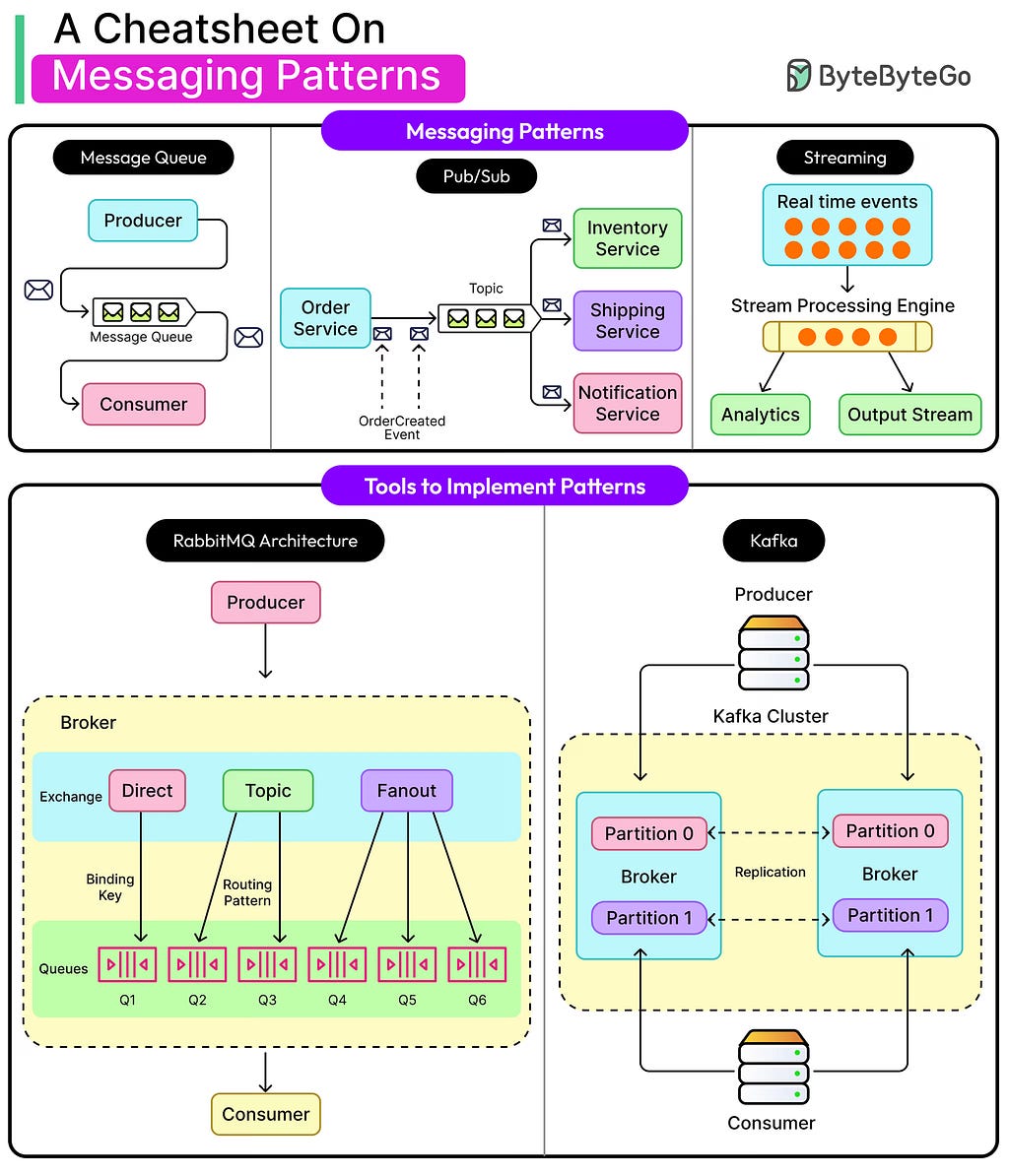
Hello guys, If you’ve ever struggled to explain how a system like Netflix, WhatsApp, or Uber scales to millions of users, you’re not alone. System Design is one of the hardest areas to master for software engineers — not because it’s impossible, but because it’s abstract.
That’s exactly where ByteByteGo comes in.
Founded by Alex Xu and Sahn Lam, ByteByteGo has transformed the way engineers learn system design — through beautiful visuals, real-world examples, and step-by-step explanations.
Their System Design Interview books and visual courses are among the most trusted resources for FAANG-level interview prep.
Recently, they’ve launched a 50% lifetime discount on their platform, making it the perfect time to invest in mastering system design. You can explore it here:
Here is the link to join ByteByteGo now — 50% discount on ByteByteGo

In this article, I’ll walk you through 10 essential system design patterns every developer should know — all inspired by the visual clarity of ByteByteGo’s approach.
10 System Design Patterns Every Software Engineer Should Know
Without any further ado, here are the 10 essential System Design Pattern which every developer should know and remember, not just for interviews but also for day-to-day software engineering and design work
1. Load Balancer Pattern
When millions of requests hit your service, a Load Balancer distributes the traffic evenly across multiple servers.
It ensures high availability, scalability, and fault tolerance.
Think of it as a “traffic cop” for your backend — directing cars (requests) to less crowded lanes (servers).
Where it’s used: Web servers, microservices, API gateways.
ByteByteGo visual insight: 6 ways to use load balancers from traffic distribution to high availability.

2. Caching Pattern
Caching stores frequently accessed data in memory to reduce database load and latency.
Without caching, every user request hits the database — creating bottlenecks.
Where it’s used: CDN, Redis, Memcached, browser caches.
ByteByteGo explains: Trade-offs between read-through, write-through, and write-back caching strategies.

3. Database Sharding Pattern
When one database can’t handle all your data, sharding partitions it horizontally into smaller chunks called shards.
Each shard handles part of the data, allowing horizontal scaling.
Challenges: Rebalancing, cross-shard queries, and consistent hashing.
Learn visually: ByteByteGo diagrams make sharding architectures intuitive, especially how routing works.

4. Message Queue Pattern
Instead of direct service-to-service calls, systems use message queues like Kafka or RabbitMQ to handle asynchronous communication.
It decouples producers and consumers — allowing systems to stay resilient under high load.
Example: Payment processing or notification systems.
Why it matters: It’s a foundation of event-driven architecture, one of the most frequent interview topics.

5. Database Replication Pattern
Replication creates multiple copies of the same database — improving availability and read scalability.
If one replica fails, another can take over without downtime.
ByteByteGo visualizes: Replication lag, Sync vs Async replication, Single Leader Replication, Leaderless Application and multi leader replication — all explained through clear flow diagrams.

6. Rate Limiter Pattern
Rate limiters control how many requests a client can make in a given time frame.
They protect APIs from abuse, DDoS attacks, and excessive usage.
Implementation examples: Token bucket, leaky bucket algorithms.
In interviews: “Design a rate limiter” is a ByteByteGo-favorite scenario — often paired with Redis or NGINX.

7. Content Delivery Network (CDN) Pattern
A CDN caches static assets (like images, CSS, videos) closer to the user’s location.
It drastically reduces latency and server load.
ByteByteGo’s take: They show how edge caching, invalidation, and TTL work behind global services like YouTube and Netflix.

8. Microservices Pattern
Large monolithic systems are broken down into smaller, independent services.
Each microservice owns its data and functionality.
Why it’s important: It’s the foundation of modern cloud architecture and interview questions like “Design Amazon” or “Design Spotify”
Learn visually: ByteByteGo’s diagrams clarify inter-service communication, discovery, and event-driven flow.

9. Observer (Pub/Sub) Pattern
This pattern allows services to publish events and others to subscribe to them asynchronously.
It enables real-time updates and decoupled communication.
Use cases: Notifications, analytics, IoT.
ByteByteGo visual: Perfectly illustrates how event buses manage complex async workflows.

10. API Gateway Pattern
The API Gateway acts as the single entry point for all client requests.
It handles routing, authentication, and rate limiting before forwarding requests to internal services.
ByteByteGo perspective: Shows how gateways integrate with microservices and load balancers to handle millions of API calls daily.

Wrapping Up — Learn System Design Visually and Effectively
These patterns form the core building blocks of modern distributed systems — and ByteByteGo teaches them like no one else.
Whether you’re preparing for your FAANG system design interview, or building real-world systems, ByteByteGo’s visual and structured approach is a complete solution.
They not only cover these 10 patterns, but also hundreds of real-world systems — from designing Instagram to scaling chat apps like Slack.
👉 Grab ByteByteGo’s Lifetime Plan at 50% OFF and start learning System Design the visual way — faster, deeper, and smarter.

Other Programming and Interview Articles you may like
- ByteByteGo vs LeetCode? which one is better for tech interview?
- ByteByteGo Lifetime Plan Review: Is It the Best Investment for Developers in 2025?
- 25 Software Design Interview Questions for Programmers
- How Algomonster helped me to master DSA for interviews?
- Exponent 70% OFF — Is It Worth It for FAANG Interview Prep?
- LeetCode vs. AlgoMonster? Which One Should You Use for Coding Interviews?
- Why System Design Is the Hardest Part of FAANG Interviews?
- How to Prepare for Coding Interviews?
- Algomonster Review 2025 — Is it worth it?
- ByteByteGo vs NeetCode vs Educative? which one is better?
- Codemia.io Annual vs. Lifetime Plan?
- Is ByteByteGo a good place for Coding interviews?
- AlgoMonster vs Exponent vs DesignGurus?
- Codemia.io 65% OFF Lifetime Plan — Is It Worth It for FAANG Interview?
- Is DesignGuru’s System Design Course worth it
- 3 Free Books and Courses for System Design Interviews
- Is System Design Interview RoadMap by DesignGuru worth it?
- Is Exponent’s System Design Course worth it?
- LeetCode vs AlgoMonster? Which is better for Coding Interview?
- 10 Best Places to Learn System Design in 2025
- My Favorite Software Design Courses for 2025
- ByteByteGo 50% OFF? Should you Join?
- 10 Reasons to Learn System Design in 2025
Thanks for reading this article so far. If you like this article then please share them with your friends and colleagues. If you have any questions or feedback, then please drop a note.
P. S. — If you just want to do one thing at this moment, go join ByteByteGo and start learning System Design and Coding Interview concepts, you will thank me later. The FAANG dream job you always wanted is not far anymore.
System Design · Coding · Behavioral · Machine Learning Interviews
10 System Design Patterns That Actually Matters (Inspired by ByteByteGo) was originally published in Javarevisited on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This post first appeared on Read More

