Why is Nginx So Popular? A Deep Dive into Its Key Features
From handling massive traffic to serving static content, understand the key features that make Nginx indispensable.

Hello friends, in a world where web applications demand lightning-fast performance and the ability to handle massive traffic, Nginx has emerged as a dominant force.
Nginx isn’t just another web server; it’s a powerhouse that fuels much of the modern internet. Understanding its architecture and key features is essential for anyone building or managing web applications.
Reliability, scalability, and flexibility — these are the hallmarks of Nginx, and the reasons why it’s become so popular.
Whether you are running a high-traffic website, deploying a load balancer, or setting up a reverse proxy, Nginx is often the first choice. But what makes Nginx so widely adopted by developers and enterprises?
But what makes it so popular?
In this article, we will deep dive into the core features that set Nginx apart, revealing how its event-driven architecture, powerful load balancing, and efficient resource utilization solve critical challenges for developers and system administrators alike.
We will try to go beyond the surface, revealing the key features that make Nginx a game-changer for web application performance, covering its architecture, high-performance web server capabilities, reverse proxy features, SSL termination, and caching mechanisms.
5 Reasons which makes Nginx a popular choices for Web Server in System Design
Whether you’re serving static content, building complex APIs, or handling millions of concurrent connections, Nginx is likely to be a part of the solution.
What’s the secret behind Nginx’s meteoric rise to prominence? It’s not just a web server; it’s a high-performance engine that powers a significant portion of the internet.
Let’s do a deep dive into Nginx’s key features, revealing the architectural decisions and design choices that make it so efficient, reliable, and popular.
1. Nginx’s Efficient Architecture
Nginx uses an advanced master-worker process model that enhances efficiency and scalability.
How It Works
- The Master Process handles configuration loading and manages worker processes.
- Multiple Worker Processes execute client requests in parallel, utilizing event-driven, asynchronous processing instead of traditional thread-based models.
Why It Matters?
- High concurrency: Nginx can handle thousands of simultaneous connections efficiently.
- Non-blocking architecture: Unlike Apache, which spawns a new thread per request, Nginx processes multiple requests asynchronously.
- Low resource usage: It consumes fewer CPU and memory resources compared to traditional web servers.
Example Use Case: Large-scale websites like Airbnb and Netflix rely on Nginx’s architecture to handle millions of requests per second.
Here is a simplified diagram explaining Nginx architecture:

2. Nginx as a High-Performance Web Server
Nginx is optimized to serve static content with minimal latency, making it ideal for high-traffic websites.
How It Works
- Handles requests using an event-driven approach instead of spawning new processes for each request.
- Caches frequently accessed static content, such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files, in memory.
- Supports gzip compression, HTTP/2, and optimized connection handling for faster page loads.
Why It Matters?
- Handles high traffic effortlessly: Unlike traditional web servers, Nginx scales without bottlenecks.
- Fast content delivery: Caching and optimized request handling reduce load times.
- Ideal for microservices: Nginx efficiently routes requests to backend services.
Example Use Case: Facebook and Instagram use Nginx to serve millions of static files with ultra-low latency.
Here is how you can use Nginx as web server:

3. Nginx as a Reverse Proxy and Load Balancer
Nginx is widely used as a reverse proxy to manage and distribute incoming traffic efficiently.
How It Works
- Nginx sits in front of multiple backend servers and forwards client requests to the appropriate server.
- It load balances traffic across multiple backend instances to prevent any single server from being overloaded.
- Supports various load-balancing algorithms, including round-robin, least connections, and IP hash.
Why It Matters?
- Distributes traffic efficiently, ensuring high availability.
- Improves security by hiding backend servers from direct exposure to clients.
- Reduces server load, enhancing performance.
👉 Example Use Case: E-commerce websites like Amazon use Nginx to manage high volumes of incoming traffic and balance the load across multiple data centers.
Here is an architecture which shows NGINX as load balancer:

4. SSL Termination with Nginx
Managing SSL encryption and decryption can be CPU-intensive for backend servers. Nginx offloads SSL/TLS processing, improving performance.
How It Works
- Nginx terminates SSL connections and forwards decrypted requests to backend servers over HTTP.
- Supports automatic HTTPS redirection, helping secure applications.
- Works with Let’s Encrypt for free SSL certificate management.
Why It Matters?
- Reduces backend load by offloading SSL processing.
- Enhances security with modern TLS encryption standards.
- Simplifies SSL certificate management for applications.
Example Use Case: Banking and fintech applications use Nginx for SSL termination to secure millions of sensitive transactions daily.

5. Content Caching with Nginx
Caching is critical for improving website performance and reducing server load. Nginx has built-in caching mechanisms that speed up content delivery.
How It Works
- Stores frequently requested content in a proxy cache, reducing the need for repeated backend requests.
- Uses a cache manager and cache loader to efficiently manage cache data.
- Supports cache expiration policies, ensuring only fresh content is served.
Why It Matters?
- Accelerates website performance by serving cached content instantly.
- Reduces backend server load, improving scalability.
- Enhances user experience with faster response times.
Example Use Case: Media streaming services like YouTube and Twitch use Nginx caching to deliver high-quality video content with minimal buffering.
Here is how you can configure Nginx as content cache server:
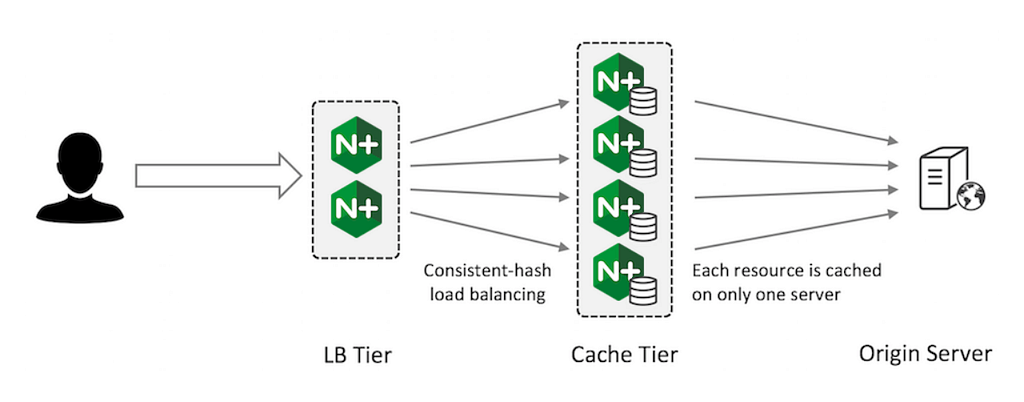
Nginx’s versatility, efficiency, and high performance make it the go-to choice for web hosting, microservices, and cloud-based applications.
Final Thoughts: Why Choose Nginx?
In short, Nginx’s popularity stems from its ability to deliver exceptional performance, reliability, and flexibility. Whether you’re building a small website or a large-scale distributed system, Nginx offers a powerful and efficient solution.
With millions of websites and enterprises relying on Nginx, it definitely is a concept and tool worth learning.
Why is Nginx So Popular? A Deep Dive into Its Key Features was originally published in Javarevisited on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This post first appeared on Read More

